Introduction:
Tuberculosis (TB), caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex, remains a significant global health challenge, demanding precise and efficient diagnostic tools for effective disease management. This comprehensive guide navigates the latest innovations in TB diagnostics, drawing upon scientific evidence to elucidate cutting-edge methodologies and essential products tailored for scientists, researchers, and veterinarians dedicated to TB control.
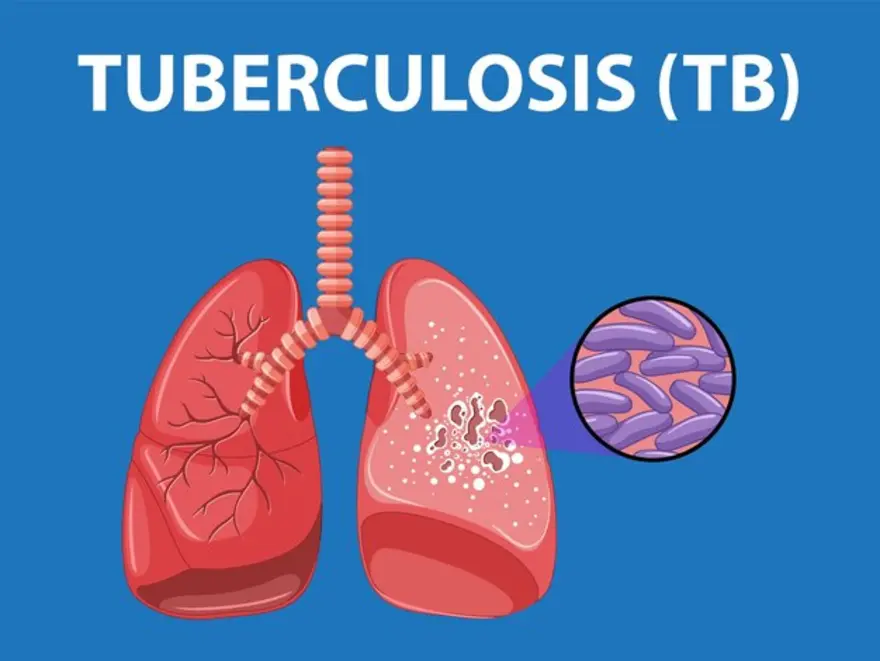
Understanding Tuberculosis:
TB, characterized by its intricate host-pathogen interactions, presents diagnostic challenges due to its diverse clinical manifestations and the emergence of drug-resistant strains. Insights from studies such as those by Pai et al. (2019) and Ryu et al. (2015) underscore the importance of molecular and immunological approaches in enhancing diagnostic accuracy and informing treatment decisions.
Advanced Diagnostic Solutions:
Scientific advancements have revolutionized TB diagnostics, offering a spectrum of sensitive and specific tools for rapid case detection, drug susceptibility testing, and epidemiological surveillance. Rapid tests and Ab tests or nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs), including Truenat® RT-PCR MTB-RIF, and serological assays such as LAM ELISA demonstrate superior sensitivity and specificity, as highlighted in studies by Lawn et al. (2012) and Denkinger et al. (2019), facilitating timely intervention and outbreak containment.
Promoting Essential Products:
Essential TB diagnostic products play a pivotal role in translating scientific knowledge into actionable solutions. Sample preparation kits optimized for diverse specimen types, high-fidelity PCR assays targeting specific genetic loci of M. tuberculosis, and culture media formulations supporting mycobacterial growth are indispensable components of the TB diagnostic armamentarium. Studies by Pang et al. (2020) and Inbaraj LR et al. (2023) emphasize the critical role of these products in ensuring standardized, reproducible diagnostic workflows.
Precision and Efficiency:
Integration of advanced technologies, including real-time PCR, next-generation sequencing, and mass spectrometry, enhances diagnostic precision and efficiency. Platforms such as the Truenat® RT-PCR MTB-RIF Ultra assay and MALDI-TOF MS demonstrate superior analytical sensitivity and rapid turnaround times, enabling early detection of TB infection and identification of drug-resistant strains, as demonstrated in studies by Zhang et al. (2006) and Kozel et al. (2017).
Clinical and Veterinary Impact:
In both clinical and veterinary contexts, advanced TB diagnostics have far-reaching implications for patient care, disease surveillance, and public health. By facilitating early case detection, optimizing treatment regimens, and identifying transmission hotspots, these diagnostics contribute to improved clinical outcomes, reduced disease burden, and enhanced zoonotic disease control strategies. Studies by Weerdenburg et al. (2020) provide valuable insights into the clinical and veterinary impact of TB diagnostics.
Empowering Collaboration:
Collaborative efforts between researchers, clinicians, veterinarians, and industry stakeholders like Gentaur are essential for driving innovation and addressing unmet needs in TB diagnostics. Through interdisciplinary collaboration, knowledge exchange, and technology transfer initiatives, we can accelerate the translation of scientific discoveries into impactful diagnostic solutions, ultimately advancing TB control efforts on a global scale. Studies by Ntinginya et al. (2019) underscore the importance of collaborative approaches in advancing TB diagnostics.
Conclusion:
As TB continues to exert a heavy toll on human and animal populations, the imperative for accurate, efficient, and accessible diagnostics has never been greater. By harnessing the power of scientific evidence and embracing innovative diagnostic solutions, scientists, researchers, and veterinarians can strengthen their diagnostic armamentarium, mitigate the spread of TB, and ultimately, improve health outcomes for individuals and communities worldwide.

